Which of the Following Is the Major Motor Tract
Although they originate. Which of the following generalizations does not describe the cerebral cortex.

Corticospinal Tract Blue Conveying Motor Signals From Motor Cortex To Download Scientific Diagram
Central processing unit CPU.

. Any injury to these tracts is known as UMN lesions. The corticospinal tract maintains connections with multiple regions of the cerebrum primarily the motor cortexThe motor cortex is recognized to have three main components the primary motor cortex premotor cortex and the supplementary motor area each of these maintain their own unique connections and methods of communication with the. The ascending tracts carry sensory information from the body like pain for example up the spinal cord to the brain.
Decussation of pyramids refers to crossover of major motor tracts in the _____ region of the brain. Intermediate zone Ventral horn PNS Fig. A medulla oblongata B pons C thalamus D mid.
Feel the tone of the muscle flaccid clonic normal. Injury to UMNs in these tracts is common because of the large areas covered by the motor neuron pathway. A disk drive stores data by __________ encoding it onto a.
The medial reticulospinal tract arises from the pons. The pyramidal tract is the primary tract that propagates signals necessary for voluntary movement. Which of the following is a major motor tract.
Central processing unit CPU. It inhibits voluntary movements and reduces muscle tone. Which of the following are motor areas of the cerebral cortex that lie in the posterior part of the frontal lobes and control voluntary movement.
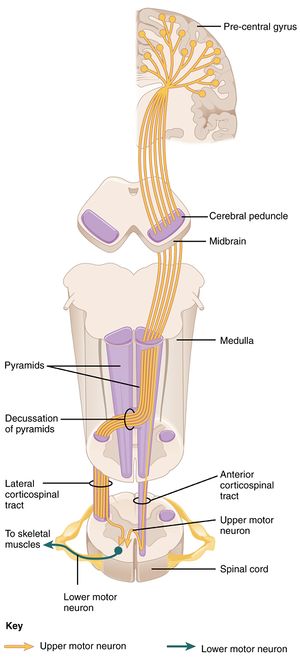
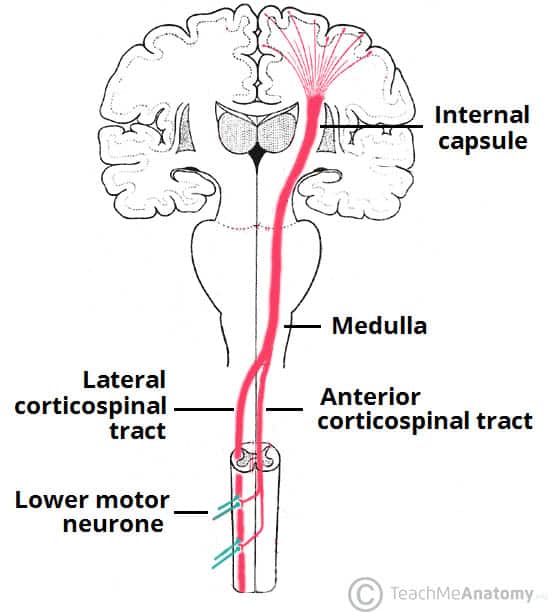
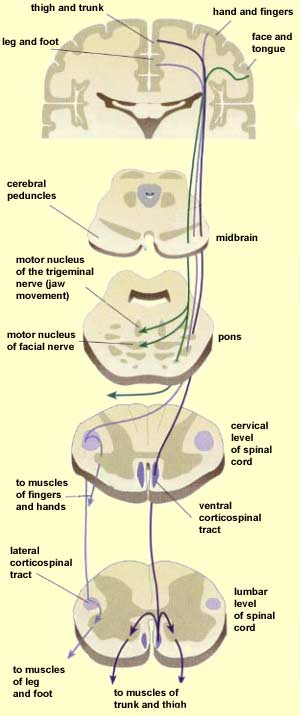
The pyramidal tract divides into the corticospinal tract and the corticobulbar tract. As the fibres emerge they decussate. In order to achieve spinal anesthesia Novocain is injected into the.
Motor system organization Motor programs for voluntary movement Descending motor pathways Motor Systems Cortical motor areas Basal ganglia Cerebellum Descending brain stem paths Descending cortical motor paths Spinal cord. The spinal cordthe ventral horns composed of motor neurons. Other tracts are named after the part of the brainstem from which they originate.
The rubrospinal tract originates from the red nucleus a midbrain structure. Robyn Hughes Tanner Marshall MS Evan Debevec-McKenney. Controls the comprehension of language.
Test the strength of the muscle group. The reticulospinal and rubrospinal tracts contain extrapyramidal motor fibres which originate in the midbrain. In human nervous system.
The anterior column contains the following. The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway running from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. Descending tracts carry motor information like instructions to move the arm.
These tracts all carry motor fibres to the spinal cord that allow for unconscious reflexive or responsive movement of muscles to control balance locomotion posture and tone. Contains major descending voluntary motor tracts for precise movements. The corticospinal tract innervates the musculature of the body apart from the head and neck and receives input from the primary motor cortex premotor cortex supplementary motor area and somatosensory area.
There are four tracts. The corticospinal tracts are considered direct because they extend directly from upper motor neurons in thecerebral cortex to lower motor neurons in the spinal cord a similar direct tract extends to lower motor neurons in the brainstem. Primary somatosensory area for receiving input from touch receptors.
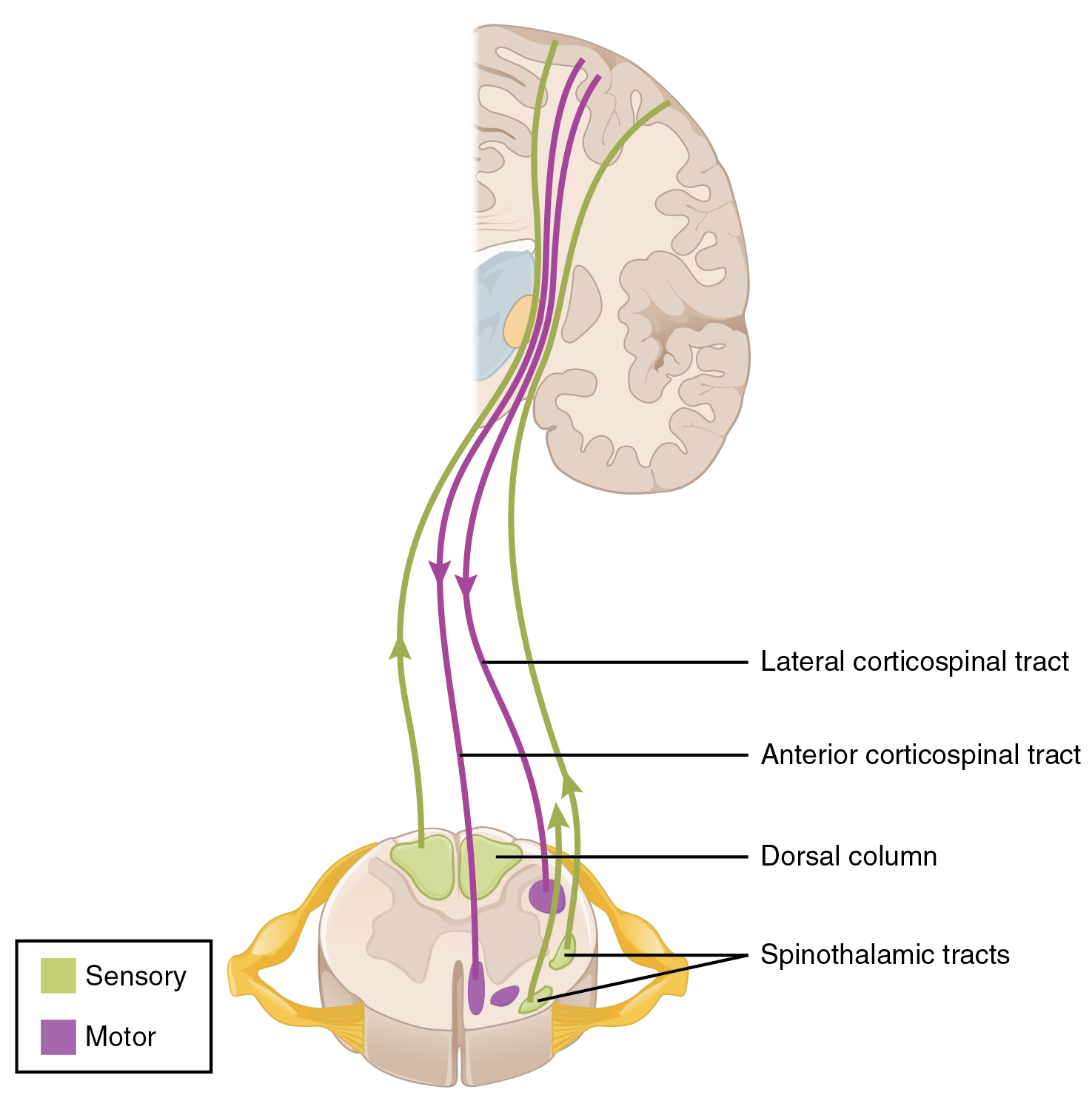
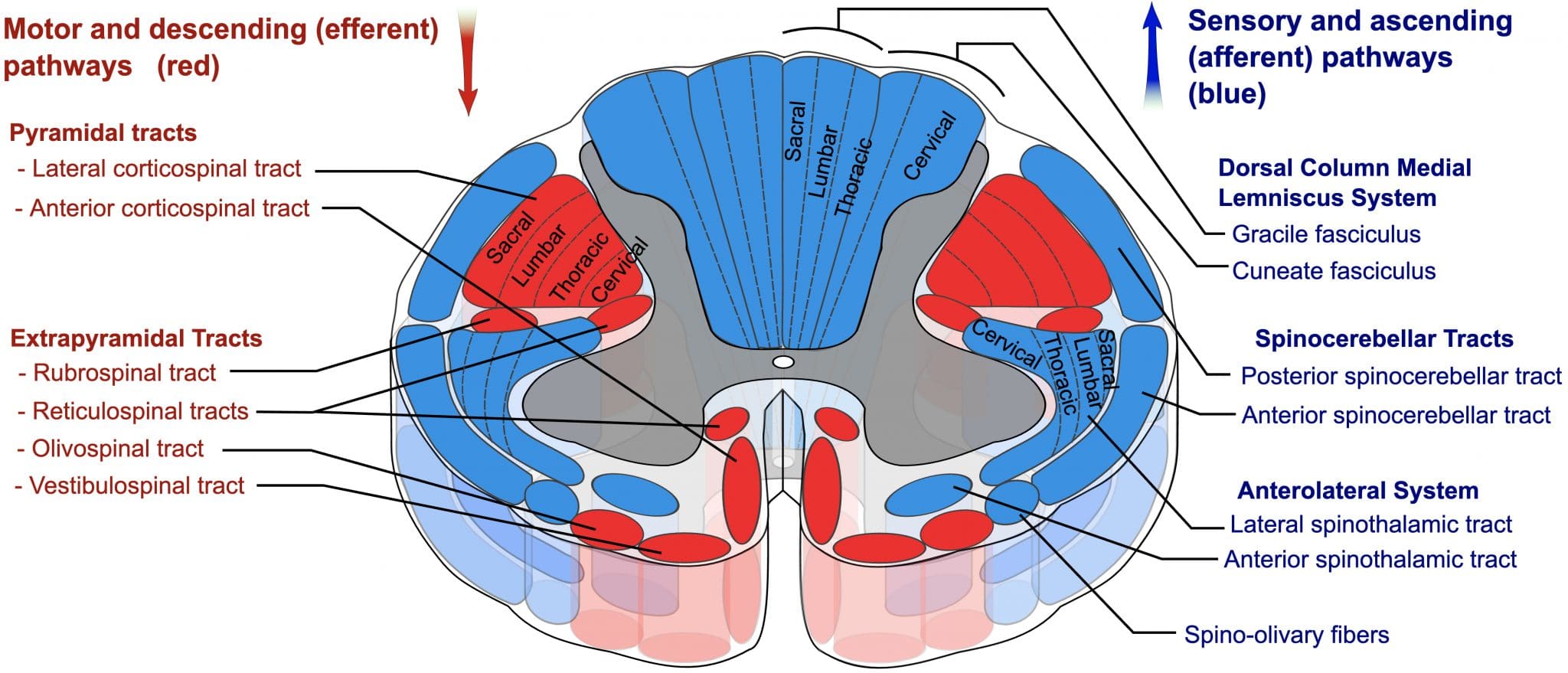
The posterior column tract. The dorsal or posterior funiculi lying between the dorsal horns. The white matter forming the ascending and descending spinal tracts is grouped in three paired funiculi or sectors.
It facilitates voluntary movements and increases muscle tone. Systematically examine all of the major muscle groups of the body. The __________ is the part of the computer that actually runs programs and is the most important component in a computer.
The cell body of these neurons are found within the. For each muscle group. Reticulospinal Vestibulospinal Rubrospinal Tectospinal Reticulospinal tracts The reticulospinal tracts do not decussate.
Axons from the corticospinal tract CSTor pyramidal tract carry information from the precentral gyrus brodmann area 4 of the motor cortex the supplemental and premotor cortices area 6 to Lower motor neurons LMNs which will synapse with muscle cells in. Which of the following statements accurately defines the functions of the cerebellum. The path starts in the motor cortex where the bodies of the first-order neuron lie pyramidal cells of Betz.
Sensory and Motor Tracts The three major sensory tracts involve chains of neurons. 2012 Pearson Education Inc. No muscle contraction is detected.
This pathway is responsible for the voluntary movements of the limbs and trunk. Which of the following is the best description of a motor tract. The main function of the Gastrointestinal System is to derive essential nutrients including proteins vitamins carbohydrates etc from the food by processing it and supplying them to other organs and body systems for their proper functioning.
33-12 Muscle Functional Hierarchy of Motor Paths Motor execution. Note the appearance or muscularity of the muscle wasted highly developed normal. Group of neurons forming tracts.
In terms of basic anatomy the overall ascending pathway is made up of three different types of neuronsFirstly there are first order neurons which receive sensory information from the receptors and send them to sensory neurons present in the posterior gray horns of spinal cord. The lateral funiculi lying on each side of the spinal cord between the dorsal-root entry. The anterior corticospinal uncrossed pyramidal tract is a small tract the fibres of which originate in the cerebral motor cortex of the same side and descend without medullary decussation.
A Each hemisphere is chiefly concerned with sensory and motor functions of the contralateral side of the body. Sensory and Motor Tracts There are three major sensory tracts. The lateral reticulospinal tract arises from the medulla.
Ascending and descending spinal tracts are pathways that carry information up and down the spinal cord between brain and body. The GI system has two major components.

Motor Areas Pyramidal System Ppt Video Online Download

Rubrospinal Tract Physiopedia Universal Access To Physiotherapy Knowledge Medical Anatomy Medical Knowledge Nervous System Anatomy
Corticospinal Tract Physiopedia

Accessphysiotherapy Motor Pathways

Accessphysiotherapy Motor Pathways
Biol 237 Class Notes The Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves

Organization Of The Human Corticospinal Tract Mn Groups Vulnerable Download Scientific Diagram

16 Major Sensory And Motor Systems Spinothalamic Tract Medical Anatomy Nursing Study
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/lateral-corticospinal-tract/rnJ5nWZvJTxYtOSGVf4fjA_Lateral_corticospinal_tract.png)
Pyramidal Tracts Corticospinal And Corticonuclear Tracts Kenhub

Corticospinal Tract Blue Conveying Motor Signals From Motor Cortex To Download Scientific Diagram
2 Minute Neuroscience Corticospinal Tract Youtube
The Sensory And Motor Exams Anatomy And Physiology
The Descending Tracts Pyramidal Teachmeanatomy

Major Ascending And Descending Tracts In The Spinal Cord Sciencedirect
The Descending Tracts Of The Central Nervous System Geeky Medics

Accessphysiotherapy Motor Pathways

Accessphysiotherapy Motor Pathways

Spinal Cord Ascending Descending Tracts Spinal Cord Nursing Study Spinal
Comments
Post a Comment